Guide: Updating the Test Bed
Track |
|---|
This guide walks you through the process of updating a Test Bed instance to the latest release.
What you will achieve
At the end of this guide you will have updated a Test Bed instance to the latest Test Bed release. The update process assumes that your target instance has been installed using either Docker or Kubernetes as described in the installation guide for development or for production.
What you will need
About 5 minutes.
A text editor (if new configuration is needed).
A web browser.
A working Test Bed installation based on Docker or Kubernetes.
Command line access to the machine hosting the Test Bed.
Access to the internet (from the host machine).
How to complete this guide
Completing the update steps will be done by issuing commands on a command line interface. All commands are provided and explained in each relevant step.
Steps
Carry out the following steps to update your Test Bed instance.
Step 1: Update the Test Bed
Depending on how your Test Bed instance was installed, follow the section for a Docker-based, or Kubernetes-based installation. Note that upgrading to a newer release requires no manual migration actions, and newer releases are always guaranteed to be backwards compatible.
Warning
Updating to 1.13.0+: When updating from a release prior to 1.13.0 to a release starting from 1.13.0, the database container itb-mysql
may take several minutes to update. Make sure you do not stop itb-mysql before this upgrade completes.
Updating a Docker-based installation
Open a command prompt and go to the folder containing your docker-compose.yml file. From here, and in case your container images
are set to a fixed release tag (e.g. isaitb/gitb-ui:1.24.3) update these to refer to the latest release:
services:
gitb-redis:
image: isaitb/gitb-redis:1.27.4
...
gitb-mysql:
image: isaitb/gitb-mysql:1.27.4
...
gitb-srv:
image: isaitb/gitb-srv:1.27.4
...
gitb-ui:
image: isaitb/gitb-ui:1.27.4
...
If you are referring to the latest or nightly tags no change is necessary. Once you are ready issue:
docker compose pull
This command will check the Docker Hub for each of the Test Bed’s components and will proceed to download newer versions as needed. Note that executing this command has no effect on your currently running Test Bed instance. To apply the new release issue:
docker compose up -d
To ensure the Test Bed is successfully updated check the logs of the itb-srv and itb-ui containers. For itb-srv issue
docker logs -f itb-srv for which you should see in the end:
> docker logs -f itb-srv
...
31/01/2025 15:36:51 INFO c.g.t.c.TestbedServiceContextListener - [] Started ITB test engine (itb-srv) - release 1.27.4
_____ _______ ____ _
|_ _|__ __| _ \ | |
| | | | | |_) | _ __ ___ __ _ __| |_ _
| | | | | _ < | '__/ _ \/ _` |/ _` | | | |
_| |_ | | | |_) | | | | __/ (_| | (_| | |_| |
|_____| |_| |____/ |_| \___|\__,_|\__,_|\__, |
__/ |
|___/
Exit the log display using CTRL-C. Then check itb-ui by issuing docker logs -f itb-ui for which the output should complete
as follows (note also the listed release number and date):
> docker logs -f itb-ui
...
31/01/2025 15:36:52 INFO hooks.PostStartHook - Started ITB frontend (itb-ui) in production mode - release 1.27.4 (2025-08-11 09:35:19)
_____ _______ ____ _
|_ _|__ __| _ \ | |
| | | | | |_) | _ __ ___ __ _ __| |_ _
| | | | | _ < | '__/ _ \/ _` |/ _` | | | |
_| |_ | | | |_) | | | | __/ (_| | (_| | |_| |
|_____| |_| |____/ |_| \___|\__,_|\__,_|\__, |
__/ |
|___/
Once again exit the log display by issuing CTRL-C. Your Test Bed should now be online and updated to the latest release.
Updating a Kubernetes-based installation
Note
This section assumes use of the Helm package manager and the Test Bed’s Helm chart. If you are using manifest files follow the instructions listed here.
If you haven’t added the Test Bed’s chart repository to your Helm installation, do this by issuing:
helm repo add itb https://www.itb.ec.europa.eu/helm
With the Test Bed’s repository added you can pull the latest chart definition by issuing:
helm repo update itb
This command will pull the latest chart definitions, including the one for the latest Test Bed release.
Assuming you have defined an override.yaml file for your instance’s configuration,
open a command prompt and go to the folder containing it. In case you have specified here image tags for a specific release
(e.g. isaitb/gitb-ui:1.24.3), update these to refer to the latest one:
redis:
image: isaitb/gitb-redis:1.27.4
...
mysql:
image: isaitb/gitb-mysql:1.27.4
...
srv:
image: isaitb/gitb-srv:1.27.4
...
ui:
image: isaitb/gitb-ui:1.27.4
...
Alternatively if you are referring to the latest or nightly tags you need to make sure that Helm pulls their latest definitions.
You can force this by setting the image pull policy to “Always” as follows (considering itb-ui as an example):
ui:
image: isaitb/gitb-ui:nightly
imagePullPolicy: Always
...
Once you have made the above changes, or in case you never set image tags in your override.yaml file, you are ready to proceed with
the update. To do this issue:
helm upgrade itb itb/itb -f override.yaml -n itb
Optionally, as part of the update, you may also choose to check the provenance and integrity of the chart by verifying its signature. A failed signature verification will prevent the update from proceeding. To do so:
If you haven’t done this before, add to your PGP keyring the Test Bed’s
public PGP key.Add to your
helm upgradecommand the--verifyflag, adding also--keyring <path_to_keyring>if your keyring is not at the default location.
Once the update completes successfully you will see the Test Bed’s post-installation notes. These will also include the number of the installed release:
> helm upgrade itb itb/itb -f override.yaml -n itb
Release "itb" has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
NAME: itb
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Nov 28 10:32:46 2024
NAMESPACE: itb
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 4
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
___ _____ ____ _ ___
|_ _||_ _|| __ ) ___ _ __ | | __( _ ) ___
| | | | | _ \ / _ \ | '_ \ | |/ // _ \ / __|
| | | | | |_) | | (_) || | | | | <| (_) |\__ \
|___| |_| |____/ \___/ |_| |_| |_|\_\\___/ |___/
The Interoperability Test Bed (ITB) is now deployed on your cluster (release "1.27.4").
...
To ensure the Test Bed has completed its initialisation you should check the logs of itb-srv and itb-ui. For itb-srv issue kubectl logs -f deployment/itb-srv -n itb
for which you should see output completing as follows:
> kubectl logs -f deployment/itb-srv -n itb
...
31/01/2025 15:36:51 INFO c.g.t.c.TestbedServiceContextListener - [] Started ITB test engine (itb-srv) - release 1.27.4
_____ _______ ____ _
|_ _|__ __| _ \ | |
| | | | | |_) | _ __ ___ __ _ __| |_ _
| | | | | _ < | '__/ _ \/ _` |/ _` | | | |
_| |_ | | | |_) | | | | __/ (_| | (_| | |_| |
|_____| |_| |____/ |_| \___|\__,_|\__,_|\__, |
__/ |
|___/
You can exit the log display by issuing a CTRL-C. To check itb-ui issue kubectl logs -f deployment/itb-ui -n itb for
which the output should complete as follows (note also the listed release number and date):
> kubectl logs -f deployment/itb-ui -n itb
...
31/01/2025 15:36:52 INFO hooks.PostStartHook - Started ITB frontend (itb-ui) in production mode - release 1.27.4 (2025-08-07 09:35:19)
_____ _______ ____ _
|_ _|__ __| _ \ | |
| | | | | |_) | _ __ ___ __ _ __| |_ _
| | | | | _ < | '__/ _ \/ _` |/ _` | | | |
_| |_ | | | |_) | | | | __/ (_| | (_| | |_| |
|_____| |_| |____/ |_| \___|\__,_|\__,_|\__, |
__/ |
|___/
Once again exit the log display by issuing CTRL-C. Your Test Bed should now be online and updated to the latest release.
Using manifest files
If you have directly used manifest files to install the Test Bed you will need to ensure they are updated for the new release.
Open a command prompt and go to the folder containing your manifest files. In case you have specified in your deployment manifests
image tags for a specific release (e.g. isaitb/gitb-ui:1.24.3) update these to refer to the latest release.
Assuming you have used the Test Bed’s manifests, these would be:
03-mysql-deployment.yamlfor theitb-mysqlcomponent.
05-redis-deployment.yamlfor theitb-rediscomponent.
07-srv-deployment.yamlfor theitb-srvcomponent.
09-ui-deployment.yamlfor theitb-uicomponent.
Ensure here that the container image is updated to the latest release (taking 09-ui-deployment.yaml as an example):
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: "itb-ui"
spec:
...
template:
...
spec:
containers:
- image: "isaitb/gitb-ui:1.27.4"
...
In case you are referring in the deployment manifests to the latest or nightly tags, you need to ensure these will
be pulled. You can force this by changing in each manifest the image pull policy to “Always” as follows:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: "itb-ui"
spec:
...
template:
...
spec:
containers:
- image: "isaitb/gitb-ui:nightly"
imagePullPolicy: "Always"
...
You can proceed with updating your Test Bed instance. Update itb-mysql by issuing …
kubectl apply -f 03-mysql-deployment.yaml
… followed by itb-srv by issuing …
kubectl apply -f 07-srv-deployment.yaml
… and finally itb-ui by issuing:
kubectl apply -f 09-ui-deployment.yaml
To ensure the Test Bed has completed its initialisation you should check the logs of itb-srv and itb-ui as described in
the previous section.
Step 2: Verify the new release
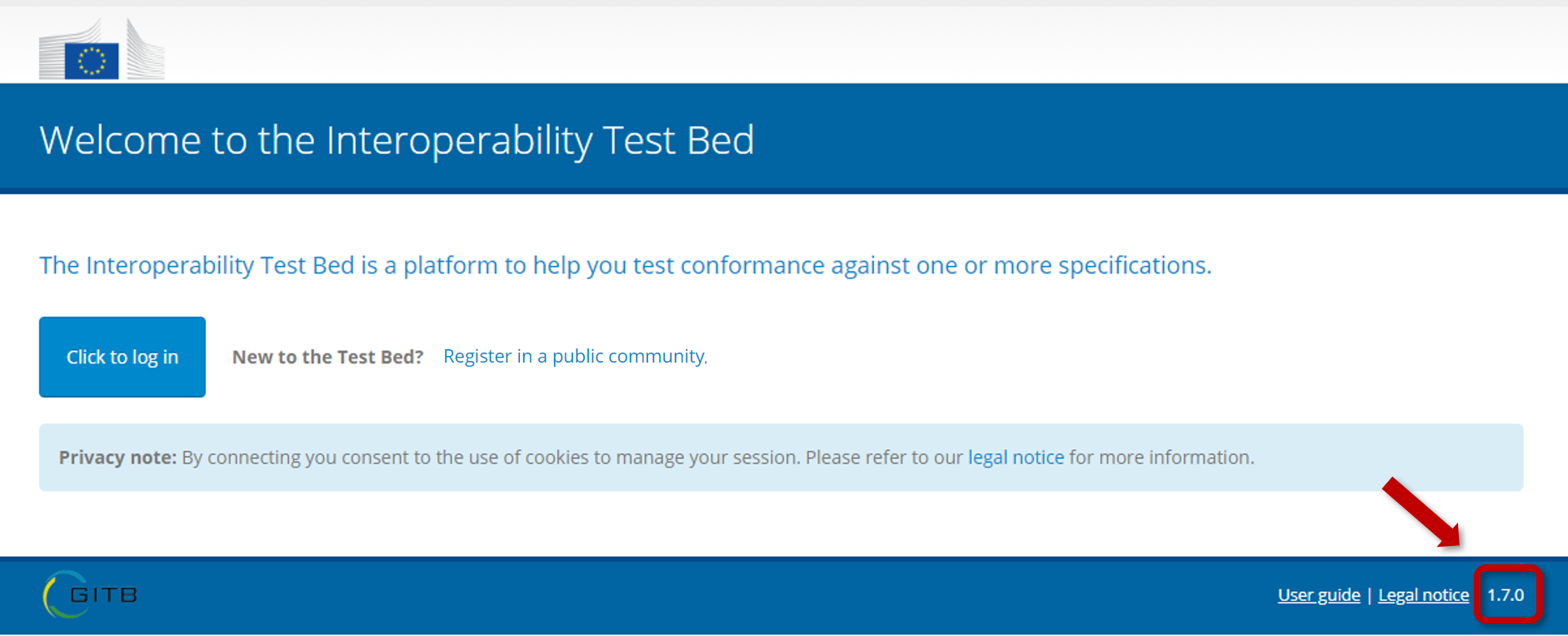
To check that the new release has been successfully installed you can also verify the version number displayed on the Test Bed’s interface. To do this visit the Test Bed’s welcome page where you will find the version number in the bottom right corner.
Summary
Congratulations! You have just updated your Test Bed to the latest version. In doing so you downloaded the Test Bed’s latest component versions, applied configuration changes, and confirmed that the update completed successfully.
See also
For more information on the Docker and Docker Compose tools, commands and properties used in this guide, check out the Docker online documentation. Further information on Helm and Kubernetes can similarly be found in their respective documentation.
In terms of relevant guides, be sure to check:
Guide: Installing the Test Bed for development use for step-by-step instructions on how to install a development Test Bed instance.
Guide: Installing the Test Bed for production use for step-by-step instructions on how to install a production Test Bed instance.